What is a Compression Fracture?
Compression fractures are defined as fracture of the vertebral column that occurs in the setting where a healthy bone would not have broken. Compression fractures are most common in patients who have weaker bones or osteoporosis.
 What symptoms does a compression fracture cause?
What symptoms does a compression fracture cause?
Compression fractures cause back pain in the location of the fracture. This may cause increased difficulty with mobility or difficulty carrying out activities of daily living due to the pain.
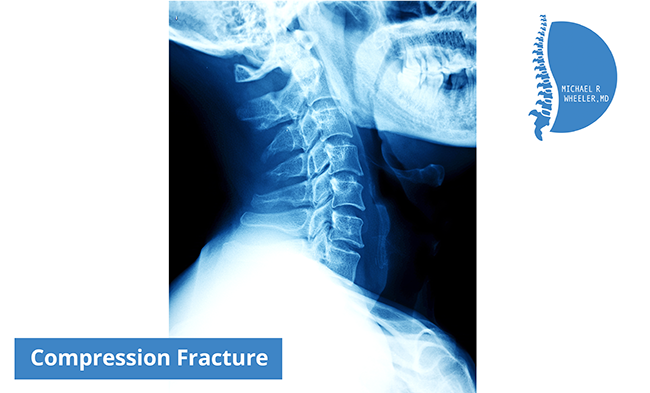
How is a compression fractures diagnosed?
Most compression fractures can be seen on plain x-rays. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan may be used to further evaluate the fracture if x-rays are inconclusive.
What is the treatment for compression fracture?
The majority of compression fractures will heal on their own and do not require any intervention. Sometimes bracing can be used to help stabilize the bone and allow for support. The most important therapy is treatment of the underlying weakened bone. In fact, a compression fracture alone is enough to diagnose the patient with osteoporosis and should warrant pharmacologic treatment in addition to supplemental calcium and vitamin D. Patients with a compression fracture should meet with his/her primary care doctor or endocrinologist to go over the medication options to treat osteoporosis.
The majority of compression fractures will heal without intervention. In a select group of patients, a procedure called a kyphoplasty can be performed to help restore the structural integrity and height of the compressed vertebra.



